
DB 구성과 Spring boot로 백엔드를 테스트해보자.
DB 테이블 만들기
CREATE USER 'ecommerceapp'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'ecommerceapp';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON * . * TO 'ecommerceapp'@'localhost';
ALTER USER 'ecommerceapp'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'ecommerceapp';유저와 권한을 부여하고 전환한다.
DROP SCHEMA IF EXISTS `full-stack-ecommerce`;
CREATE SCHEMA `full-stack-ecommerce`;
USE `full-stack-ecommerce` ;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `full-sproducttack-ecommerce`.`product_category` (
`id` BIGINT(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`category_name` VARCHAR(255) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`))
ENGINE=InnoDB
AUTO_INCREMENT = 1;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `full-stack-ecommerce`.`product` (
`id` BIGINT(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`sku` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`name` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`description` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`unit_price` DECIMAL(13,2) DEFAULT NULL,
`image_url` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`active` BIT DEFAULT 1,
`units_in_stock` INT(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`date_created` DATETIME(6) DEFAULT NULL,
`last_updated` DATETIME(6) DEFAULT NULL,
`category_id` BIGINT(20) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `fk_category` (`category_id`),
CONSTRAINT `fk_category` FOREIGN KEY (`category_id`) REFERENCES `product_category` (`id`)
)
ENGINE=InnoDB
AUTO_INCREMENT = 1;
INSERT INTO product_category(category_name) VALUES ('BOOKS');
INSERT INTO product (sku, name, description, image_url, active, units_in_stock,
unit_price, category_id, date_created)
VALUES ('BOOK-TECH-1000', 'JavaScript - The Fun Parts', 'Learn JavaScript',
'assets/images/products/placeholder.png'
,1,100,19.99,1, NOW());
INSERT INTO product (sku, name, description, image_url, active, units_in_stock,
unit_price, category_id, date_created)
VALUES ('BOOK-TECH-1001', 'Spring Framework Tutorial', 'Learn Spring',
'assets/images/products/placeholder.png'
,1,100,29.99,1, NOW());
INSERT INTO product (sku, name, description, image_url, active, units_in_stock,
unit_price, category_id, date_created)
VALUES ('BOOK-TECH-1002', 'Kubernetes - Deploying Containers', 'Learn Kubernetes',
'assets/images/products/placeholder.png'
,1,100,24.99,1, NOW());
INSERT INTO product (sku, name, description, image_url, active, units_in_stock,
unit_price, category_id, date_created)
VALUES ('BOOK-TECH-1003', 'Internet of Things (IoT) - Getting Started', 'Learn IoT',
'assets/images/products/placeholder.png'
,1,100,29.99,1, NOW());
INSERT INTO product (sku, name, description, image_url, active, units_in_stock,
unit_price, category_id, date_created)
VALUES ('BOOK-TECH-1004', 'The Go Programming Language: A to Z', 'Learn Go',
'assets/images/products/placeholder.png'
,1,100,24.99,1, NOW());스키마와 테이블 만들고 insert 쿼리로 데이터 입력
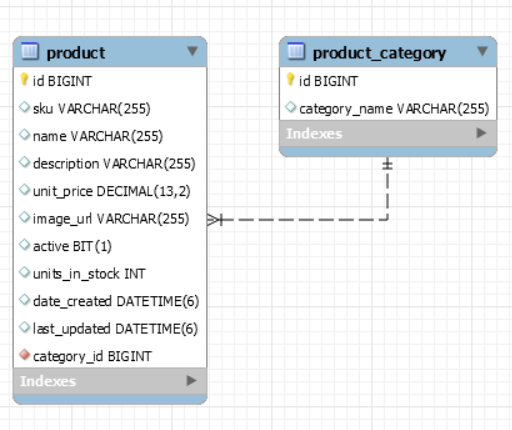
테이블이 생긴다.
스프링부트 설정

사이트에서 생성하고 이클립스에서 불러오기
처음 불러 왔을 때 모습
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/full-stack-ecommerce?useSSL=false&useUnicode=yes&characterEncoding=UTF-8&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&serverTimezone=UTC
spring.datasource.username=ecommerceapp
spring.datasource.password=ecommerceapp
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL8Dialect
spring.data.rest.base-path=/apiapplication.properties 파일에 이런 내용 추가
데이터베이스 접속 정보
Entity 생성
package com.seol.ecommerce.entity;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import org.hibernate.annotations.CreationTimestamp;
import org.hibernate.annotations.UpdateTimestamp;
import lombok.Data;
@Entity
@Table(name="product")
@Data
public class Product {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name="id")
private Long id;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name="category_id", nullable= false)
private ProductCategory category;
@Column(name="sku")
private String sku;
@Column(name="name")
private String name;
@Column(name="description")
private String description;
@Column(name="unit_price")
private BigDecimal unitPrice;
@Column(name="image_url")
private String imgaeUrl;
@Column(name="active")
private boolean active;
@Column(name="units_in_stock")
private int unitsInStock;
@Column(name="date_created")
@CreationTimestamp
private Date dateCreated;
@Column(name="last_updated")
@UpdateTimestamp
private Date lastUpdated;
}
@CreationTimestamp와 @UpdateTimestamp는 Hibernate가 처리하는 Annotation이다.
하지만 무엇을 개발자대신 처리하는지 확실하지 않으니 자세한 공부가 필요하다.
package com.seol.ecommerce.entity;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import lombok.Data;
@Entity
@Table(name="product_category")
@Data
public class ProductCategory {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name="id")
private Long id;
@Column(name="category_name")
private String categoryName;
@OneToMany(cascade=CascadeType.ALL, mappedBy="category")
private Set<Product> products;
}
REST API
| HttpMethod | Path | CRUD |
| POST | /products | Create |
| GET | /products | Read list of products |
| GET | /products/{id} | Read single product |
| PUT | /products/{id} | Update |
| DELETE | /products/{id} | Delete |
dao 패키지와 인터페이스를 생성한다.
Repository를 만든다.
package com.seol.ecommerce.dao;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import com.seol.ecommerce.entity.Product;
public interface ProductRepository extends JpaRepository<Product, Long>{
}package com.seol.ecommerce.dao;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.rest.core.annotation.RepositoryRestResource;
import com.seol.ecommerce.entity.ProductCategory;
@RepositoryRestResource(collectionResourceRel = "productCategory", path = "product-category")
public interface ProductCategoryRepository extends JpaRepository<ProductCategory, Long>{
}
collectionResourceRel은 JSON 엔트리 이름이다.
path는 /product-category 이다.
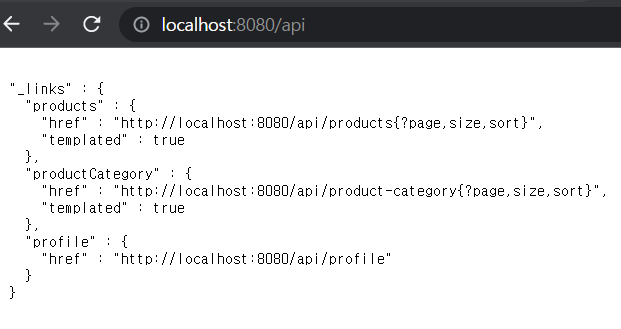


REST API Read only
REST API의 모든 메서드를 사용하고 싶지 않고 읽는 것만 하고싶다.
두 가지 방법이 있는데
1. Spring Data REST를 사용하지 않고 @RestController를 구성하여 @GetMapping을 정의하는 방법. 이 방법은 Spring Data REST의 페이징이나 소트 기능 사용 못 함
2. Spring Data REST 를 사용하는 방법. POST, PUT, DELETE 기능을 끈다.
package com.seol.ecommerce.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.rest.core.config.RepositoryRestConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.config.RepositoryRestConfigurer;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.CorsRegistry;
import com.seol.ecommerce.entity.Product;
import com.seol.ecommerce.entity.ProductCategory;
@Configuration
public class MyDataRestConfig implements RepositoryRestConfigurer {
@Override
public void configureRepositoryRestConfiguration(RepositoryRestConfiguration config, CorsRegistry cors) {
HttpMethod[] theUnsupportedActions = { HttpMethod.PUT, HttpMethod.POST, HttpMethod.DELETE };
//Product의 HTTP 메소드 금지 : PUT, POST, DELETE
config.getExposureConfiguration()
.forDomainType(Product.class)
.withItemExposure((metdata, httpMethods) -> httpMethods.disable(theUnsupportedActions))
.withCollectionExposure((metdata, httpMethods) -> httpMethods.disable(theUnsupportedActions));
//ProductCategory의 HTTP 메소드 금지 : PUT, POST, DELETE
config.getExposureConfiguration().forDomainType(ProductCategory.class)
.withItemExposure((metdata, httpMethods) -> httpMethods.disable(theUnsupportedActions))
.withCollectionExposure((metdata, httpMethods) -> httpMethods.disable(theUnsupportedActions));
}
}
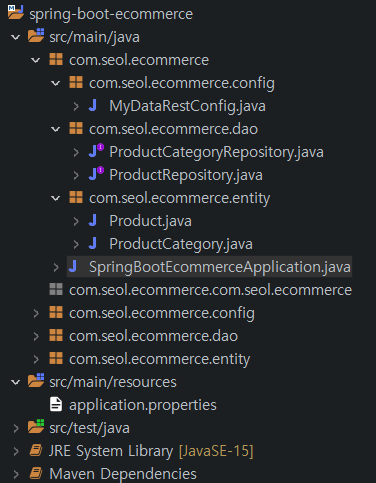
config 패키지를 만들고 class를 만든다. 인터페이스를 구현한다.


Postman으로 테스트하면 405 오류가 나면서 거절된다.
'컴퓨터공학 > Boot & Angular' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Angular> Online Shop Template 적용 (0) | 2022.01.23 |
|---|---|
| Angular> Front end - Product List (0) | 2022.01.22 |
| Angular> Bootstrap 적용, 조건문, 서식 (0) | 2022.01.16 |
| Angular> 기본 작동 방식 (0) | 2022.01.15 |
| Angular> Create Project (0) | 2022.01.13 |



